M3AE: Multimodal Representation Learning for Brain Tumor Segmentation with Missing Modalities
摘要
提出SimCLR,用于视觉表征的对比学习,简化了最近提出的对比自监督学习算法,为了理解是什么使对比预测任务能够学习有用的表示,系统研究了提出框架的主要组成部分,发现:
(1)数据增强的组成在定义有效的预测任务中起着关键的作用
(2)在表示和对比损失之间引入一个可学习的非线性变换,大大提高了已学习表示的质量
(3)与监督学习相比,对比学习受益于更大的批量规模和更多的训练步骤
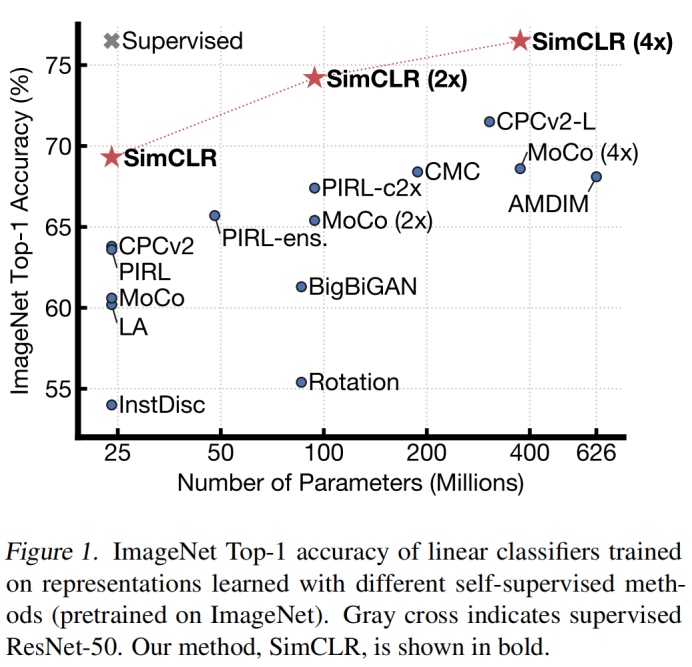
SimCLR学习的自监督表示训练的线性分类器达到了76.5%的top-1精度,比之前的技术水平提高了7%,与监督ResNet-50的性能相匹配。
方法
- 对比学习框架
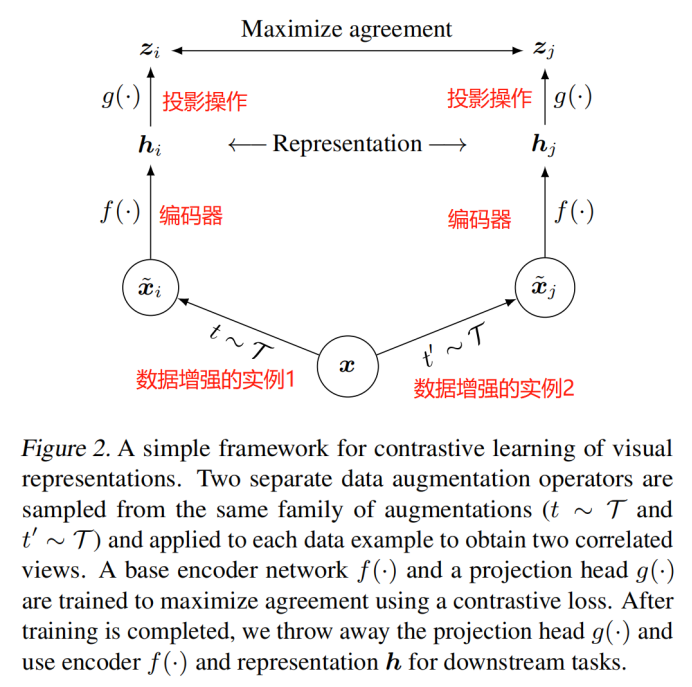
随机采样一个minibatch的数据(N个样本),定义生成的增强样本对的对比预测任务,得到2N个数据点,给定一个正例对,将其它2(N-1)个增强样本当作负例,相似性度量采用余弦距离,则正例对(i,j)的损失函数为:
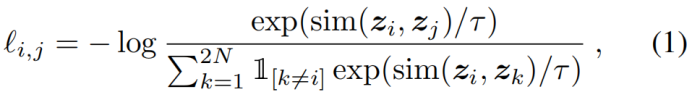
τ代表温度参数,最后的损失是计算所有正例样本对,包含(i,j)和(j,i),称之为NT-Xent (the normalized temperature-scaled cross entropy loss)
提出的方法可总结为:

实验
1. 投影头实验发现:
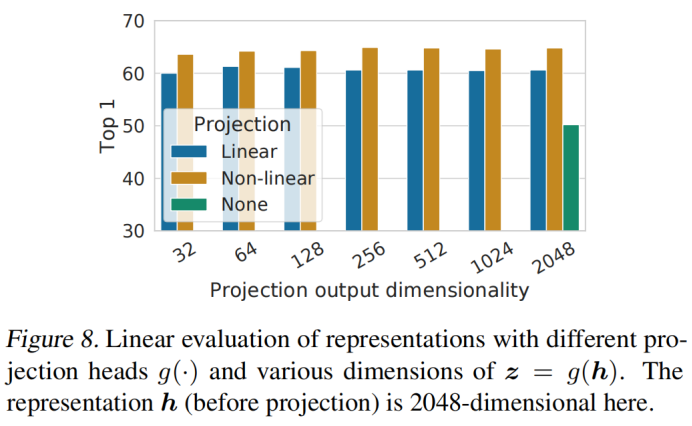
- 非线性投影比线性投影好(>3%),比不投影高很多(>10%)
- 隐藏层在投影头前面比在层后面要好
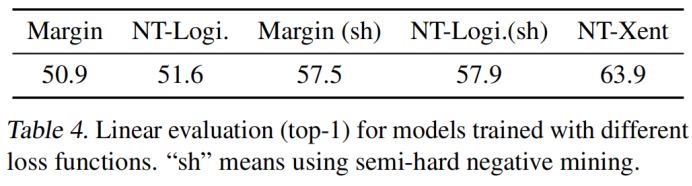
2. NT-Xent损失与其它常用对比损失函数的比较(logistic loss、margin loss):
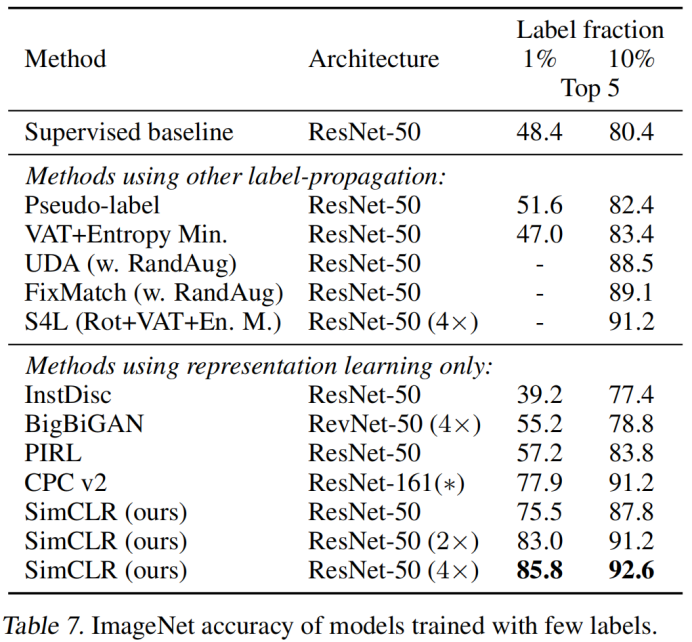
3. 采用不同标签训练时的指标对比:
公众号

过去已逝,未来太远,只争今朝